Melanoma is a serious type of skin cancer that starts in melanocytes, the cells that give your skin its color. While it is less common than other skin cancers, melanoma is more likely to grow and spread quickly, which makes early detection especially important. When found and treated early, most people recover well.
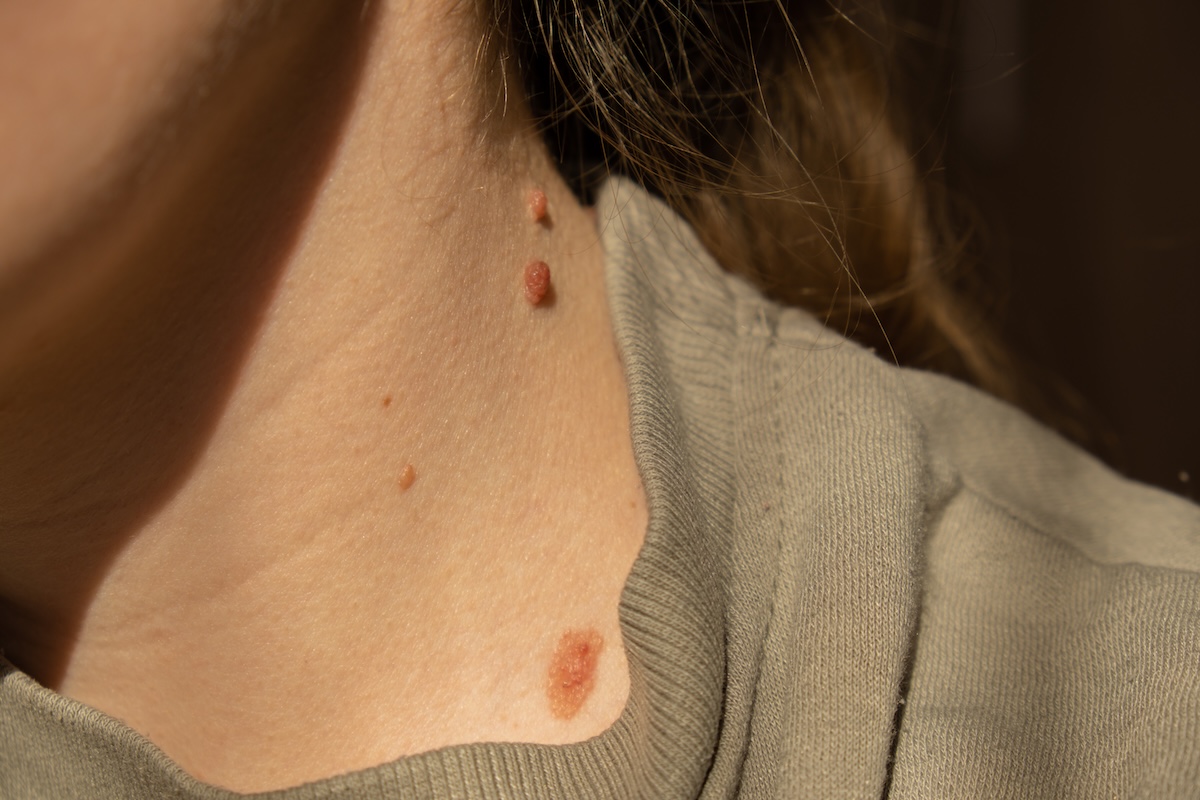
Melanoma can appear anywhere on the body, including places that don’t get a lot of sun, like the soles of the feet or under fingernails. It can also start in existing moles or form as a new spot. Knowing what to look for and how to treat it can save lives.
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma begins when melanocytes start growing out of control. These cells usually help protect your skin from sun damage by producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. But when these cells become damaged, often by ultraviolet (UV) light, they can grow in ways they shouldn’t.
Most melanomas are caused by too much exposure to the sun or tanning beds. But melanoma can also happen in people who don’t spend much time in the sun or have darker skin. That’s why it’s important for everyone to pay attention to changes in their skin.
Causes of Melanoma
Melanoma is usually caused by damage to the DNA in skin cells from UV radiation. This damage builds up over time. Other possible causes include:
-
Having fair skin, light eyes, or red or blond hair
-
A history of frequent sunburns, especially during childhood
-
Spending lots of time in the sun or using tanning beds
-
Having many moles or unusual-looking moles
-
A family history of melanoma
-
A weakened immune system
Even though you can’t change some risk factors—like your skin type or family history—you can protect your skin and lower your risk by limiting UV exposure.
Types of Melanoma
There are different types of melanoma. Each one may look different and behave differently:
-
Superficial spreading melanoma: The most common type. It usually grows slowly across the surface of the skin before going deeper.
-
Nodular melanoma: A more aggressive type that grows faster and deeper from the start. It often looks like a raised bump.
-
Lentigo maligna melanoma: Often found in older adults, especially on sun-damaged skin like the face or neck. It grows slowly and starts as a flat patch.
-
Acral lentiginous melanoma: A rare type that appears on the palms, soles, or under the nails. It is more common in people with darker skin.
-
Mucosal melanoma: Also rare. It starts in moist parts of the body like the mouth, nose, or genitals.
Symptoms of Melanoma
You should watch for new spots on your skin or changes to existing moles. The “ABCDE” rule can help:
-
Asymmetry: One half doesn’t match the other.
-
Border: The edges are uneven, ragged, or blurry.
-
Color: There are several colors or shades in one spot.
-
Diameter: It’s larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser).
-
Evolving: It changes over time in size, shape, color, or how it feels.
Other symptoms can include itching, bleeding, or a sore that doesn’t heal. Not all melanomas follow these rules, so if anything on your skin looks or feels different, have it checked by a doctor.
Diagnosis
To find out if a suspicious spot is melanoma, a doctor will usually examine your skin and ask about your medical history. If melanoma is suspected, the next step is a biopsy. This means removing a small piece of skin to look at under a microscope.
If the biopsy shows melanoma, more tests may be needed to see if the cancer has spread. These might include imaging scans or checking nearby lymph nodes. The doctor will then assign a stage from 0 to IV, depending on how far the cancer has gone.
Early stages mean the cancer is only in the skin. Later stages mean it has spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment Options
The right treatment depends on the type and stage of melanoma, as well as your overall health. Common treatment options include:
-
Surgery: The most common treatment for early-stage melanoma. The surgeon removes the cancer and some healthy skin around it.
-
Immunotherapy: Helps your immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. Often used in advanced stages.
-
Targeted therapy: Uses drugs that focus on specific gene changes in melanoma cells. This treatment works best when tests show those changes are present.
-
Radiation therapy: Uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. Sometimes used after surgery or to treat spread cancer.
-
Chemotherapy: Less common for melanoma today but may be used when other treatments don’t work. It uses drugs to kill fast-growing cells.
Many people with melanoma also receive regular follow-ups to check for any signs that the cancer has returned. These check-ups are an important part of long-term care.
Living with Melanoma
A melanoma diagnosis can be scary, but many people recover fully—especially when it’s found early. After treatment, you’ll need to keep a close eye on your skin. Regular skin checks and follow-up visits with your doctor are key.
You can also take steps to lower your risk of getting melanoma again:
-
Use sunscreen every day, even when it’s cloudy.
-
Wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses.
-
Stay out of the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
-
Avoid tanning beds.
-
Check your skin once a month for new or changing spots.
Melanoma is serious, but it’s also one of the most treatable cancers when caught early. By understanding the signs, protecting your skin, and seeing a doctor when something looks off, you can take control of your health.

